Liriope’s Muse: Tree Care Tips from a Master Arborist
TRUSTED TREE CARE SERVICES SINCE 1970
Liriopes Muse: The Role of Trees in Carbon Sequestration
I have a deep appreciation for the many ways trees benefit our environment. One of their most significant contributions is their ability to sequester carbon dioxide (CO₂), a major greenhouse gas responsible for climate. In this blog post, I’ll delve into what carbon sequestration is, how trees contribute to it, and why it’s vital for our planet’s health.
What is Carbon Sequestration?
Carbon sequestration refers to the process of capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2). This can occur naturally, through processes such as photosynthesis in trees and other plants, or artificially, through technological solutions. By removing CO2 from the atmosphere and storing it, carbon sequestration helps mitigate the greenhouse effect and global warming.
How Do Trees Sequester Carbon?
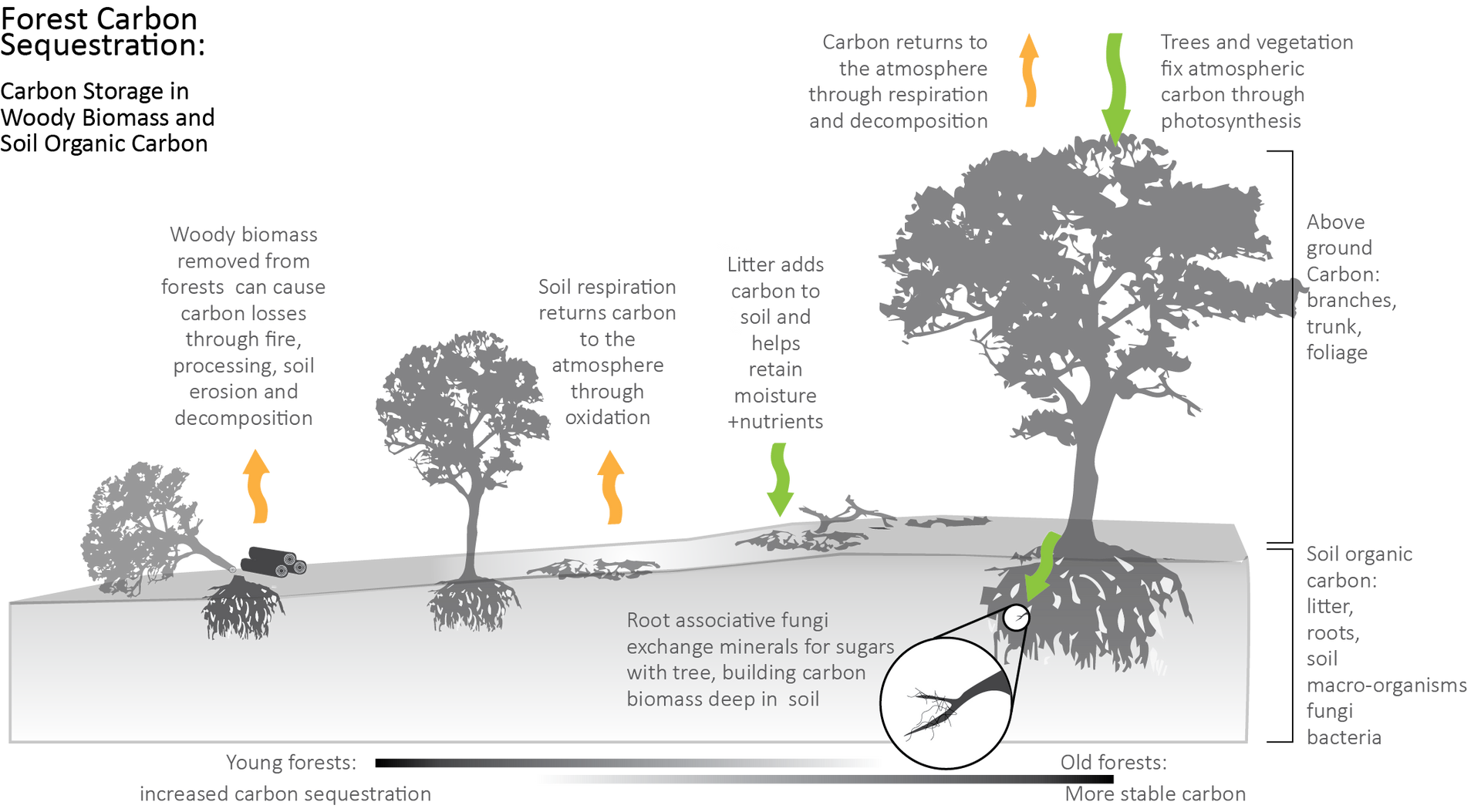
Trees sequester carbon through photosynthesis, the process by which they convert CO2 and sunlight into energy (glucose) and oxygen and store it in their roots, trunk, and foliage. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how it works:
- Photosynthesis: Trees absorb CO₂ from the air through small openings in their leaves called stomata. Using sunlight, trees convert CO₂ and water into glucose (a form of sugar) and oxygen through the process of photosynthesis. The glucose is used for growth and energy, while the oxygen is released back into the atmosphere.
- Biomass Accumulation: The carbon absorbed by trees is stored in various parts of the tree. As trees grow, they accumulate more biomass, thus storing more carbon. A single mature tree can absorb and store significant amounts of carbon over its lifetime.
- Soil Carbon Storage: Trees also contribute to carbon storage in the soil. Dead leaves, branches, and roots decompose and become part of the soil organic matter. Additionally, tree roots interact with soil microbes, enhancing soil structure and increasing its ability to store carbon.
A single mature tree can absorb as much as 48 pounds of CO2 per year. Over its lifetime, this can add up to several tons of carbon dioxide sequestered and kept out of the atmosphere.
Why is Carbon Sequestration Vital?
- Climate Regulation: By absorbing CO₂ from the atmosphere, trees help reduce the overall concentration of greenhouse gases. This, in turn, helps mitigate the effects of climate change, such as global warming and extreme weather events.
- Improving Air Quality: Trees not only sequester carbon but also filter pollutants from the air, improving overall air quality.
- Biodiversity: Forests and trees provide habitat for a wide range of species. By promoting tree growth and forest conservation, we also protect biodiversity, which is essential for ecosystem resilience and human well-being.
- Enhancing Soil Health: Trees improve soil health by preventing erosion, enhancing water retention, and promoting nutrient cycling. Healthy soils are more productive and better able to support diverse plant and animal life.
- Human Well-being: Trees contribute to human health and well-being by providing clean air, reducing heat in urban areas, and offering recreational spaces.
Maximizing the Role of Trees in Carbon Sequestration
To maximize the benefits of trees in carbon sequestration, it’s important to consider several factors:
- Tree Species Selection: Different species sequester carbon at different rates. Fast-growing trees, such as poplars and willows, can sequester carbon quickly, while long-lived, slow-growing species like oaks and pines sequester carbon over a longer period.
- Forest Management: Sustainable forest management practices, such as selective logging and reforestation, ensure that forests remain healthy and continue to sequester carbon efficiently.
- Urban Tree Planting: Planting trees in urban areas can significantly contribute to carbon sequestration while also providing shade, reducing heat islands, and improving the quality of life for residents.
- Reforestation and Afforestation: Reforesting degraded lands and afforesting areas that were not previously forested can significantly increase carbon sequestration. These efforts should prioritize diverse, multi-species plantings to enhance ecosystem health.
- Protecting Existing Forests: Preventing deforestation and promoting conservation efforts are crucial for maintaining the carbon sequestration potential of existing forests.
Trees are invaluable allies in our fight against climate change. By understanding and enhancing their role in carbon sequestration, we can make significant strides toward a more sustainable and healthier planet. I encourage everyone to support tree planting initiatives, practice sustainable tree care, and advocate for policies that protect our forests. Together, we can ensure that trees continue to play their essential role in carbon sequestration and environmental stewardship.
Liriope’s Muse - Expert Tree Care Tips